 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||

|  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
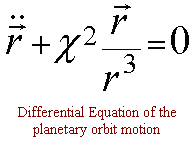 |
 |
|
|
||
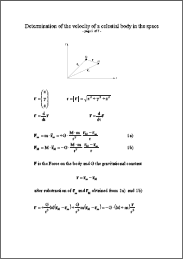
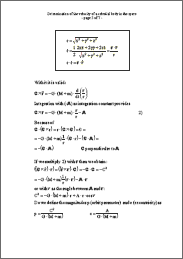
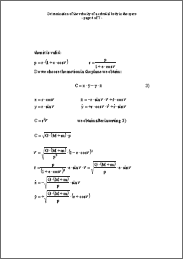
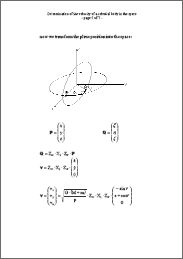
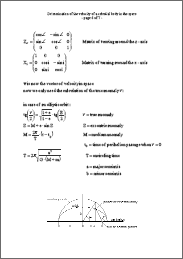
Determination of the velocity of a celestial body in the space In every point of its orbit a celestial body has a certain velocity (velocity is the vector of speed), which is a function of the position on its orbit. In the following proceeding it is described how to come from the basic equation (attraction force equals acceleration force) to the orbit in the 3-dimensional space, thereafter the velocity is determined. The absolute value of the velocity (=speed) can be used to determine the speed, for instance, of a planet or comet in the solar system (provided a central body like the sun etc). |
Betimmung der Geschwindigkeit eines Himmelskörpers im Raum In jedem Punkt seiner Umlaufbahn hat ein Himmelskörper eine Geschwindigkeit (und eine Richtung), die eine Funktion der Umlaufbahn ist. In der folgenden Abhandlung ist beschrieben, wie man von der Grundgleichung (Anziehungskraft = Beschleunigungskraft) zur Umlaufbahn kommt (im 3-dimensionalen Raum) und dann daraus die Geschwindigkeit bestimmt. Der Absolutwert der Geschwindigkeit kann verwendet werden, um z.B. die Geschwindigkeit eines Planeten oder Kometen im Sonnensystem zu bestimmen (vorausgesetzt ein Zentralkörper wie die Sonne etc). |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
Here you can get all the 6 pages combined in pdf-Format
For reading PDF-files,
you need the free PDF-Acrobat Reader, here you can download it
last update Aug 14th 2011